Hydrogen atoms can easily enter the metal and move in the lattice, and can be recombined into hydrogen molecules in some lattice defects. The volume of hydrogen molecules is 26 times that of hydrogen atoms, thus generating a pressure of up to 1000 bar in the material, resulting in defects and delayed cracks in the material. This phenomenon is called hydrogen embrittlement.
Hydrogen embrittlement will occur at the stress concentration position, such as the welding joint, especially in the heat affected zone. Therefore, the conventional hydrogen heat exchanger usually adopts the following types:
(1) Double pipe heat exchangers

1. Skid mounted with double pipe heat exchangers
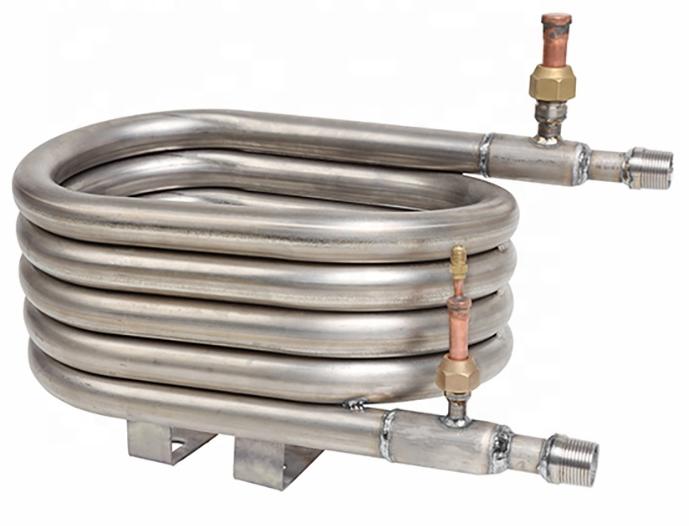

2. double pipe heat exchangers
For the double pipe heat exchanger , the high-pressure pipe side is bent from 6m/piece of steel pipe, and the thick pipe of the low-pressure shell side is welded outside the high-pressure pipe to form a concentric sleeve. Hydrogen flows in the high pressure pipe side. This structure reduces welding joints and stress concentration parts, which can avoid hydrogen embrittlement, but there are many defects. For example:
1. Overhaul, cleaning and disassembly are troublesome, and leakage is easily caused at the detachable connection.
2. Limited material selection.Welding is not allowed in the inner pipe of double pipe heat exchangers. welding will cause thermal expansion cracking. In order to save space, most of double pipe heat exchangers choose to bend and coil into coiled pipes, so many special corrosion resistant materials cannot be produced normally.
3. The double pipe heat exchanger has not yet formed a unified welding standard, and each enterprise chooses the welding method according to the experience of other heat exchange products. Therefore, various problems are common at the welding point of the double pipe heat exchanger, which requires frequent inspection and maintenance.
(2)Conventional hydrogen heat exchanger

3.conventional heat exchangers
The hydrogen cooler adopts the heat transfer principle of the conventional heat exchanger. In the structural design, the commonly used elliptical head welding structure is removed and the conventional mechanical seal connection form is adopted. However, due to the structure principle of traditional heat exchanger, with the continuous increase of design pressure, the wall thickness is continuously thickened, and the overall size and weight of the product are constantly increasing, while the heat exchange efficiency has reached the limit and cannot be broken through. Such a huge and bulky hydrogen cooler is not suitable for the planning and construction of the hydrogen refueling station, nor can it be integrated with the hydrogen dispenser to fill hydrogen for vehicles.

4.Volume Comparison between Conventional Heat Exchanger and Diffusion bonded Microchannel Heat Exchanger
(3)GOT Micro-channel H-series hydrogen cooler
GOT microchannel hydrogen cooler is a new type of high efficiency heat exchanger composed of microchannel heat exchange core, head, nozzle and flange. The heat exchange core is connected by diffusion welding process to form atomic fusion. The overall structure has no stress concentration point and no weld seam, which perfectly avoids the occurrence of hydrogen embrittlement.It has high heat exchange efficiency,small product volume and convenient maintenance.
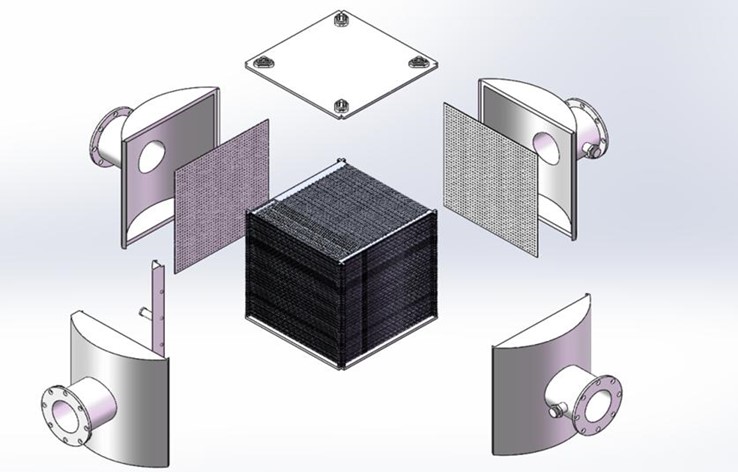
5.Structure Disassembly Diagram of GOT Micro-Channel Hydrogen Cooler
